Red clover. Kirov region
The Kirov
region is classified as an area of risky agriculture. Therefore, the focus in
agriculture is on livestock and fodder crops. Red clover is the most widespread
fodder crop in the field grasslands of the Kirov region. Since fodder fields
occupy the majority of the arable land in the region, clover flowers are
probably the most abundant flowers in the Kirov region.
Red clover (Latin: Trifolium pratense) is a plant from the genus clover (Trifolium), family Fabaceae (legumes), subfamily Faboideae (Papilionoideae).
The Latin name
of the plant translates to "three-leaved," as the three leaves are
one of its distinguishing features. Four-leaved clovers, which are famous for
being lucky charms, are much rarer.
Clover is
of great economic importance to the region due to its high yield and
nutritional and fodder value. Clover is a source of biological nitrogen
accumulation in the soil. Its roots host bacteria of the genus Rhizobium, which
assimilate molecular nitrogen and transfer it to the clover in exchange for
carbohydrates. Additionally, clover improves soil fertility, as its deep roots
extract potassium, calcium, and phosphorus from deep soil layers and leave them
in the upper arable layer.
Red clover
began to be cultivated in fields relatively recently, at the end of the XIX
century. Mass clover sowing in Vyatka started after the October Revolution. In
the Vyatka province, peasants in the Yaransky district were the first to start
sowing clover. Initially, peasants grew clover not in fields for fodder, but on
well-fertilized lands, "on corners," where manure was spread. The
goal was to produce seeds for sale. Perm and Vyatka clover seeds were highly
valued on the market for their qualities: winter hardiness, longevity, and high
yield.
They are
still valued today. Red clover seeds grown in the Kirov region are distributed
to neighboring regions and supplied to foreign countries. Clover and grass
mixtures based on it are used to prepare high-quality rough and succulent feed
for livestock (hay, haylage, silage), enabling the production of high-quality
livestock products (meat, milk, and dairy products), for which the Kirov region
is renowned.
Clover is a
valuable nectar source, but the nectar is accessible only to long-tongued bees
and bumblebees. Honey productivity is 6 kg of honey per hectare of crops. The
honey is among the best varieties and does not crystallize for a long time.
Clover
leaves are used to produce vitamin concentrates and essential oil, which is
used in aromatic compositions. Clover is used in salads, green soups, and
botvinya (a cold soup). In the past, dried and crushed leaves were added to
flour when baking rye bread, and they were also used to prepare sauces and in
cheese production.
Additionally,
clover can be used to make jam: for this, 300 grams of flower heads are boiled
for half an hour in 500 ml of boiling water with the addition of 1 kg of sugar.
The
medicinal properties of red clover are determined by its rich chemical
composition. In folk medicine, it is used for colds and coughs, inflammation of
mucous membranes, allergies, liver diseases, bronchial asthma, weakness,
exhaustion, lack of appetite, angina, headaches and dizziness, diabetes,
rheumatism, anemia, abscesses, and burns.
In
cosmetology, clover-based products are actively used to prepare moisturizing
and softening masks for the face and hair.
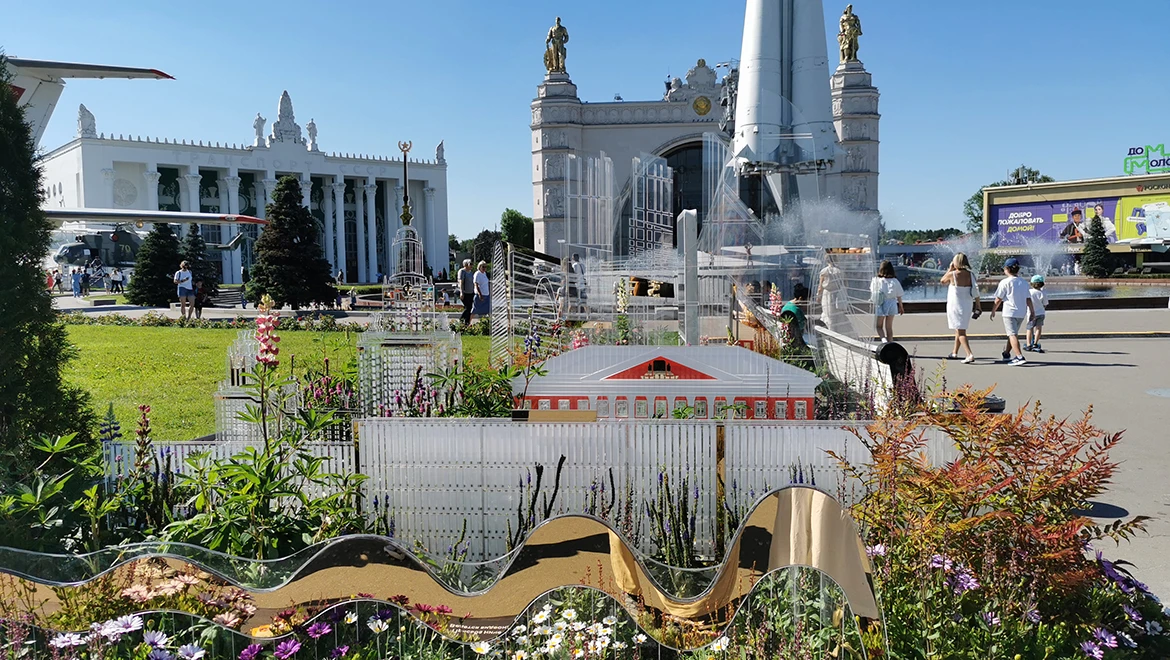
Along with the RUSSIA EXPO, the flower festival is also coming to an end.
The "Future in Flowers" festival continues at the RUSSIA EXPO, where unique flowerbeds from all regions of our country can be seen at the "Space" pavilion until July 8.
The RUSSIA EXPO concludes on July 8, and with it, the flower festival will also come to an end.